The web Browser you are currently using is unsupported, and some features of this site may not work as intended. Please update to a modern browser such as Chrome, Firefox or Edge to experience all features Michigan.gov has to offer.
Healthy Hearts

The Heart Disease and Stroke Prevention Unit, which is housed within the MDHHS Cardiovascular Health, Nutrition and Physical Activity Section, is working on establishing stroke systems of care, strengthening community-clinical linkages, enhancing team-based care, and implementing health system intervention activities.
This page includes summaries of some of the initiatives currently being worked on by the Section and its partners.
For more information about the work of the Heart Disease and Stroke Prevention Unit Secretary Kelly Garrow (e-mail: GarrowK@michigan.gov).
-
Heart Disease and Stroke Prevention Unit Focus Areas
 Forging and fostering strong partnerships with health systems, community groups, and public health entities to implement heart disease and stroke prevention and management strategies.
Forging and fostering strong partnerships with health systems, community groups, and public health entities to implement heart disease and stroke prevention and management strategies.
 Improving identification, reporting, management, and treatment of heart disease and stroke risk factors.
Improving identification, reporting, management, and treatment of heart disease and stroke risk factors.
 Building systems for near real-time surveillance of chronic conditions to intervene and offer resources to improve care coordination.
Building systems for near real-time surveillance of chronic conditions to intervene and offer resources to improve care coordination.
 Increasing awareness of heart disease and stroke risk factors, promoting linkages to evidence-based lifestyle-change programs, and working to improve cardiovascular health through partnerships with community organizations.
Increasing awareness of heart disease and stroke risk factors, promoting linkages to evidence-based lifestyle-change programs, and working to improve cardiovascular health through partnerships with community organizations.
 Addressing health disparities through interventions for populations disproportionately affected by cardiovascular risk factors and outcomes.
Addressing health disparities through interventions for populations disproportionately affected by cardiovascular risk factors and outcomes.
 Engaging partners across local and state-level entities to create a multidisciplinary learning collaborative to address the impact of social factors on cardiovascular health outcomes.
Engaging partners across local and state-level entities to create a multidisciplinary learning collaborative to address the impact of social factors on cardiovascular health outcomes.
 Co-leading the Michigan Million Hearts Initiative with the American Heart Association of Southeast Michigan to increase the effective use of clinical and community strategies to diagnose and treat people with heart disease and its risk factors.
Co-leading the Michigan Million Hearts Initiative with the American Heart Association of Southeast Michigan to increase the effective use of clinical and community strategies to diagnose and treat people with heart disease and its risk factors.
 Leading a statewide integrated stroke registry system focused on quality improvement across EMS, hospital, and discharge settings.
Leading a statewide integrated stroke registry system focused on quality improvement across EMS, hospital, and discharge settings.
 Established a state-level, multi-disciplinary Michigan Improving Cardiovascular Health (MICH) Learning Collaborative toward addressing the impacts of social factors on cardiovascular health outcomes.
Established a state-level, multi-disciplinary Michigan Improving Cardiovascular Health (MICH) Learning Collaborative toward addressing the impacts of social factors on cardiovascular health outcomes.
-
Heart Disease and Stroke Prevention Unit Projects
Million Hearts 2027 Initiative
 Million Hearts® 2027 is a national initiative co-led by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services to prevent one million heart attacks and strokes in five years. The initiative focuses partner actions on a small set of priorities selected for their impact on heart disease, stroke, and related conditions.
Million Hearts® 2027 is a national initiative co-led by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services to prevent one million heart attacks and strokes in five years. The initiative focuses partner actions on a small set of priorities selected for their impact on heart disease, stroke, and related conditions.
Michigan Million Hearts stakeholders aim to reduce and prevent heart attacks and strokes among Michigan adults through promotion of the use of team-based care, health information technology and the utilization of community health workers.► Learn more about Michigan Million Hearts.
MDHHS works collaboratively with internal and external partners, such as health care systems, providers, policy makers, community-based organizations, and key stakeholders, to support and build on actions taken to prevent and manage heart disease, stroke, and associated conditions.CDC-23-0004: The National Cardiovascular Health Program
Michigan implements evidence-based strategies to prevent and manage cardiovascular disease within high-burden populations. This includes using electronic health records (EHR) and health information technology to better identify, track, and address the clinical and social service needs of populations at highest risk for cardiovascular disease, particularly in managing hypertension and high cholesterol. Michigan continues to build our statewide chronic disease registry, CHRONICLE, by analyzing the pilot data and engaging with stakeholders. Improving cardiovascular health starts with accurate blood pressure measurement, documentation of data, and use of protocols.
To improve health outcomes and reduce disparities, our program involves refining clinical systems for reporting, recording, and monitoring out-of-office, self-measured blood pressure. Part of that system is defining EHR interactions. Another part is defining how the clinical staff (e.g., nurses, nurse practitioners, pharmacists, nutritionists, physical therapists, social workers, and community-based workers) operate within a team-based care model. We enhance team-based care by identifying team roles and understanding how each role contributes a protocol for treatment and addressing social needs.
Another significant focus is on integrating social needs assessments into clinic-level EHRs, then streamlining the identification and support for food, housing, transportation, and other health-related social needs. Partnerships with state-level and community-based organizations drive the development of coordinated multidisciplinary teams to manage patient care and address barriers to social services, such as by referring high-risk patients to community health programs.
This effort also expands access to self-measured blood pressure monitoring programs and leverages community-clinical linkages, enabling better integration of social health into clinical settings and empowering patients to take control of their health through accessible tools and community support.
Wrapped with all of this is the Michigan Improving Cardiovascular Health (MICH) Learning Collaborative — a statewide multidisciplinary partnership between a team of partners in public health, healthcare, and community to facilitate communication and the exchange of ideas toward improving blood pressure control and cardiovascular health outcomes related to hypertension, high cholesterol, and stroke, through optimizing care and influencing policy, system, and environmental change.
MICH Learning Collaborative members concentrate their collective efforts on the implementation and evaluation of evidence-based strategies that can contribute to the prevention and management of cardiovascular disease (CVD). A primary focus of the MICH Learning Collaborative is to promote multi-sector collaboration toward addressing the social and economic factors necessary for helping communities and health systems respond to social determinants present in their communities and to offer resources to those at highest risk of CVD for obtaining the best possible health outcomes.
CDC-23-0005: The Innovative Cardiovascular Health Program
The Heart Disease and Stroke Prevention (HDSP) Unit partners with organizations to reduce the risk of CVD among those most vulnerable to its ill effects. Through this grant, HDSP is focused on 17 census tracts in Detroit and five census tracts in Flint where at least 53% of the population has high blood pressure. Collaborating with clinical and community partners, we focus on reducing healthcare disparities by leveraging EHRs, health information technology (HIT), and other innovative tools, addressing social determinant of health (SDOH), and increasing participation in evidence-based lifestyle change programs, while working to reduce barriers to preventing and managing cardiovascular disease.
To provide evidence-based prevention and control support, we are enhancing the use of EHR/HIT systems to track and monitor the clinical and social service needs of patients with high blood pressure. People in Detroit can visit a mobile health unit to get their blood pressure checked and to be connected to support from a pharmacist and community health workers (CHWs). We support addressing patient social needs as identified through a standardized social needs assessment, documenting in the EHR, and using this data at a population level to inform larger resource needs.
Additionally, the project promotes the use of geo-mapping tools, such as those in Everlake and FindHelp, to identify and refer individuals to services like housing, transportation, and other essential health-related social supports. This approach ensures that vulnerable populations receive the support they need — both within and beyond the clinical setting — to care for themselves.
We are also building effective team-based care for patients by identifying team roles, supporting each staff to work at the top of their scope of practice, and assisting health systems to understand how each role fits into a protocol. We’re enhancing capacity within the prioritized census tracts through health information systems and enabling care teams to coordinate effectively for hypertension and cholesterol management. This includes using aggregated data to identify service gaps and optimize patient engagement through self-management tools and reminders.
To address broader social service barriers in the priority census tracts, we are fostering multidisciplinary partnerships, integrating CHWs and pharmacists. These partnerships support medication adherence and help connect patients to essential social services and evidence-based lifestyle change programs, ultimately improving patients' cardiovascular health.
This project also includes a Flint-based learning collaborative consisting of multidisciplinary and cross-sector stakeholders centered around the goal of addressing and implementing evidence-based or evidence-informed practices for cardiovascular disease prevention, detection, control, and management within approved priority populations of focus throughout the five Flint census tracts of highest cardiovascular disease burden.
The learning collaborative will promote shared policies and practices that continuously improve the quality of health care delivery and social care coordination in the City of Flint through engagement of stakeholders to identify and address factors that affect residents’ health, such as transportation, food insecurity, and housing, as well as access to high-quality medical care.
Michigan Stroke Program
The Michigan Stroke Program works to establish a data-driven, linked stroke data system that will be utilized to guide and inform quality improvement efforts throughout stroke systems of care in Michigan in order to prevent strokes and resulting disabilities. Michigan Stroke Program staff and partners concentrate their efforts in five areas:
- Systems capacity (building the capacity to link current silos of stroke care data to develop, integrate and improve a statewide comprehensive system of stroke care);
- Pre-hospital care (assessing and improving emergency medical services [EMS] pre-hospital care for stroke and institute concerted quality improvement efforts between EMS and hospitals);
- Post-discharge services (improving access to services needed in the post-discharge period);
- Public awareness (improving community awareness regarding stroke signs and symptoms, the importance of calling 9-1-1, and access to services for patients with stroke risk factors, such as hypertension and cholesterol); and
- Burden of stroke (reducing disparities and overall stroke burden).

-
Michigan Fact Sheets and Data
Data and surveillance reports about heart disease, stroke, and associated risk factors can be found on the Data & Statistics page on this website.
-
Online Educational Resources
Online Order Form for MDHHS Heart Disease and Stroke Prevention Unit Patient Materials
Educational materials produced by the MDHHS Heart Disease and Stroke Prevention Unit are provided free of charge to Michigan residents in quantities up to 100. (Shipping included.)
The available resources include information about sodium intake, controlling and tracking high blood pressure, and following the DASH Eating Plan with recommended daily calorie needs and daily activity levels.
MDHHS Learning Module: Hypertension
After completing this interactive, Microsoft PowerPoint-based learning module, you will be able to:
- define hypertension;
- differentiate between normal and elevated blood pressure readings;
- describe the consequences of uncontrolled hypertension; and
- identify ways to manage hypertension.
► Open the Hypertension learning module
(Please Note: This file is 22.5MB and may take a few moments to download, depending upon the speed of your Internet connection.)
MDHHS Learning Module: Cholesterol
After completing this interactive, Microsoft PowerPoint-based learning module, you will be able to:
- differentiate between the two main types of cholesterol;
- describe the consequences of high cholesterol; and
- identify ways to prevent and manage high blood cholesterol.
► Open the Cholesterol learning module
(Please Note: This file is 23.9MB and may take a few moments to download, depending upon the speed of your Internet connection.)
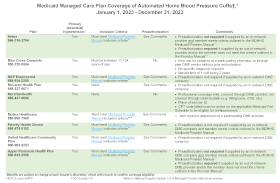
Medicaid Managed Care Plan Coverage of Automated Home Blood Pressure Cuffs
Attention clinical partners and health care professional organizations: In an effort to improve control of hypertension, reduce associated comorbidities, and decrease costs associated with health care resource utilization, the MDHHS Heart Disease and Stroke Prevention Unit promotes the use of self-measured blood pressure monitoring (SMBP). SMBP is the regular measurement of blood pressure by the patient outside the clinical setting, usually in the home. SMBP tied with clinical support has been shown to improve blood pressure in patients with hypertension.
To facilitate patient access to home blood pressure cuffs and understanding of cuff coverage benefits, the Unit has created a Medicaid home blood pressure cuff coverage grid.
 The grid can be used by health care providers to check inclusion criteria, preauthorization requirements, and special instructions specific to each managed care plan prior to prescribing blood pressure cuffs to patients with hypertension for blood pressure self-monitoring.
The grid can be used by health care providers to check inclusion criteria, preauthorization requirements, and special instructions specific to each managed care plan prior to prescribing blood pressure cuffs to patients with hypertension for blood pressure self-monitoring.
Additional Resources
Michigan Department of Health and Human Services (MDHHS)
- MDHHS Cardiovascular Health, Nutrition & Physical Activity Section website
- Michigan WISEWOMAN (Well-Integrated Screening and Evaluation for Women Across the Nation) program (MDHHS)
- MDHHS Tobacco Section website
- Michigan Tobacco Quitlink (MDHHS)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
- American Heart Month Toolkits 2022, including tools and resources for health care providers, public health professionals, and individuals and patients
- CDC Division for Heart Disease and Stroke Prevention website
- Cardiac Rehabilitation | Million Hearts
- High Blood Pressure
- High Cholesterol
- All About Sodium
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- NHLBI website
- Health Topics: High Blood Pressure
- Health Topics: High Blood Cholesterol
- Health Topics: DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) Eating Plan
American Heart Association (AHA) / American Stroke Association (ASA)
- AHA website
- ASA website
- Health Topics: High Blood Pressure
- Health Topics: Cholesterol
- Healthy Living/ Healthy Eating/ Eat Smart: Sodium
- Get with the Guidelines quality improvement programs for medical professionals
American Medical Association (AMA)
State Alliance of Michigan YMCAs (Michigan YMCA )
Return to Cardiovascular Health, Nutrition & Physical Activity Section home page
Please Note: Although we make every effort to ensure that our website is compliant with current Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) standards, some of the links on this page may lead to outside websites that are not ADA-compliant.